|
|
|
 |
|
|
Iprodione |
Action / Use
ACTION: Fungicide.
USE: For control of Alternaria, Botrytis, Fusarium, Helminthosporium, Monilinia, Rhizoctonia, Sclerotinia, Septoria, etc. Developed in many countries on vine, table grapes, fruit, almonds, berries, cereals, potatoes, vegetables, flowers, ornamentals, turf, oilseed rape, seed treatment of cereals and vegetables; crops like sugar beets, sunflower, rapeseed, and rice.
FORMULATIONS: Wettable powder, flowable.
PREMIX PARTNERS: Carbendazim; Chlorothalonil; Diniconazole; Thiophanate-methyl; Thiram. |
|
Identification |
| COMMON NAME: Iprodione (ANSI, ISO, BSI). |
|
Chemistry |
|
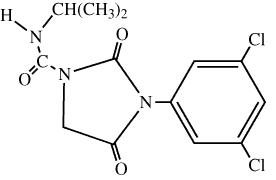
COMPOSITION: 3-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-N-(1-methylethyl)-2,4-dioxo-1-imidazolidinecarboxamide.
PROPERTIES: White, odorless, non-hygroscopic crystals. Stable under normal storage conditions. Soluble in acetone (300 g/l), benzene (200 g/l).
|
|
Environmental Guidelines |
HAZARDS: Fish: LC50 6.7 mg/l (4 day) (rainbow trout), 2.25 mg/l (bluegill). Bee: Nontoxic.
SOIL PARTICLE ADSORPTION: Low order of mobility in soil. Not persistent in soil.
WATER SOLUBILITY: Almost insoluble (13 mg/l). |
|
Safety Guidelines |
TOXICITY: (Rat): Oral LD50 >4400 mg/kg. (Rabbit): Dermal LD50 >2000 mg/kg.
HANDLING/STORAGE CAUTIONS: Do not contaminate water, food, or feed by storage or disposal of this chemical. | |
|

